Products
Contact Us
 Shandong IRO Polymer Chemicals Co., Ltd.
Shandong IRO Polymer Chemicals Co., Ltd.
Tel : +86-532-66888207
Fax: +86-532-85028486
Web: www.iropolymer.com
Email: inquiry@iropolymer.com
contact@iropolymer.com

|
Your current position: Home > Products >> Water Treatment Chemicals |
Nonionic Polyacrylamide (NPAM)
CAS No.:
9003-05-8
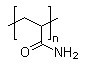
Molecular Formula:
(C3H5NO)n
Structural Formula:
Property:
Nonionic polyacrylamide (NPAM) differs from charged anionic and cationic types. Its molecular chain contains only amide groups, lacking ionic functional groups. This grants it unique application boundaries and process advantages.
Nonionic polyacrylamide is electrically neutral, unaffected by water quality fluctuations. Its molecular chains lack charged groups like -COO- or -NH3+. The zeta potential approaches 0 mV. It maintains a stable conformation across a broad range, effectively preventing “charge shielding” failure caused by sudden changes in ionic strength. It exhibits exceptional adaptability to varying water quality conditions.
Nonionic polyacrylamide primarily functions through bridging interactions, supplemented by adsorption. It exhibits outstanding shear resistance. The molecular weight of this agent typically ranges between 8~18 million. Its radius of gyration (Rg) is approximately 200~260 nm. It forms multi-point adsorption with surface groups such as -OH, -COOH, and Si-O on particles in water through “hydrogen bonds + van der Waals forces.” A single molecular chain can bridge 10~30 particles. The resulting floc has a fractal dimension Df of approximately 2.3, 0.2 higher than that of anionic polyacrylamide at equivalent concentrations. Shear resistance is correspondingly enhanced by 25~35%. Stability is maintained even under turbulent flow conditions.
Nonionic polyacrylamide (NPAM) also offers the significant advantage of broad compatibility. It exhibits no charge antagonism with commonly used water treatment chemicals such as Al/Fe salts, bipolar PAM, and magnetic seeds. It can be flexibly dosed at different stages of the treatment process. Furthermore, for complex wastewater containing high color, high salinity, high silica, and high organic matter, it consistently maintains a floc growth rate k > 0.35/min. Its applicability spans a wide range of wastewater types, providing greater flexibility for water treatment processes.
Specification:
| Products | Product Name | Degree of Hydrolysis | Molecular Weight | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonionic PAM Powder | IROFLOC100 | Low | Medium | Lead, zinc, nikel ore, etc |
| Nonionic PAM Powder | IROFLOC101 | Low | High | |
| Nonionic PAM Powder | IROFLOC134 | Low | High | Phosphate ore, copper ore,etc. |
| Nonionic PAM Powder | IROFLOC135 | Medium | High |
Application:
Nonionic polyacrylamide (NPAM) excels in three challenging water treatment scenarios. Its core advantages include resistance to salt bridging, absence of charge interference, and compatibility with high-salinity sludge.
1. Treatment of High-Salinity Complex Industrial Wastewater
For coal chemical reverse osmosis concentrate, pharmaceutical evaporation condensate, and alternating acid-alkali wastewater from silicon chemical processes—characterized by TDS levels of 15~35 g/L, SS concentrations of 500~3000 mg/L, and ζ-potential of -20 mV. The treatment sequence is as follows.
Treatment involves adjusting pH to 6.5~7.5, dosing 50~80 mg/L PAC, followed by 0.5~1.5 mg/L NPAM. Within 30 minutes, SS drops below 20 mg/L, turbidity removal exceeds 95%, and sludge volume reduces by 30%.
2. Emergency Treatment for High-Turbidity Rivers and Lakes
For raw water from rivers and lakes with NTU levels of 1000~3000 and seasonal conductivity fluctuations, no complex adjustments are required. By dosing 0.3~0.6 mg/L NPAM and 10~15 mg/L PAC at a 1.5 m/h inclined tube load, raw water NTU can be reduced below 5 NTU while extending filter operation cycles by 1.8 times.
3. Conditioning of High-Salinity Sludge
Sludge from textile dyeing and chemical plants exhibits TDS levels of 8~12 g/kg dry solids (DS). Cationic PAM often forms loose flocs due to charge shielding. Switching to 4~6 kg/t DS of NPAM combined with 20 kg/t DS of CaO reduces sludge specific resistance from 1*1013 to 4*1012 m/kg. Belt filter press capacity increases by 20%, while cake moisture content decreases further by 2-3%.
Usage:
The dissolution and dosing process of nonionic polyacrylamide (NPAM) requires strict parameter control to ensure effective performance. The key lies in precisely managing concentration, water quality, equipment, as well as the timing and dosage of addition.
1. Drug Dissolution
The drug dissolution concentration must be maintained between 0.05% and 0.1%. Excessively high concentrations may prevent complete dissolution of NPAM, while excessively low concentrations may accelerate degradation. Water used for dissolution should be soft water with a hardness level below 200 mg/L. If water hardness is high, softening treatment must be performed beforehand to prevent calcium ions in the water from reacting with the amide groups of NPAM. This prevents localized hydrolysis forming calcium carboxylate gel, which compromises efficacy.
Equipment requirements include a variable-frequency screw feeder and a low-shear agitator. Maintain a line speed of 1~1.5 m/s during mixing. Dissolution tanks should be made of PE or 304 stainless steel. Centrifugal pump circulation is strictly prohibited to avoid high shear forces damaging NPAM molecular chains.
2. Dosage Process
The dosing point should be set 3~5 seconds after PAC or iron salt addition. After dosing, first agitate rapidly at a GT value of 250/s for 1 minute. Then agitate slowly at a GT value of 40/s for 8 minutes. Ensure thorough mixing and reaction between NPAM and the water body.
Dosage must be adjusted according to the specific scenario. For high-salinity wastewater treatment, dosage ranges from 0.5~1.5 mg/L. For sludge conditioning, dosage is 4~6 kg/t DS.
When determining optimal dosage in laboratory testing, use both turbidity and ζ-potential as dual indicators. Select the dosage yielding ζ-potential ≈ -3 mV with the lowest residual turbidity to ensure optimal treatment efficacy.
Package and Storage:
25Kg/bag(Powder), 25Kg/bag(Colloid), inner bag is PVC film, outer weaved plastic bags. Keep dry.
Keywords:
Nonionic polyacrylamide; NPAM; N-PAM; Polyacrylamide; PAM; PHPA Coagulant;Flocculation; Cationic flocculant; Cationic polyelectrolyte; Cationic polymer; Cationic PAM; Cationic acrylamide copolymer; Cationic polymeric coagulant; Cationic polyelectrolytic flocculant; Cationic water-soluble polymer; Cationic emulsion polymer; Cationic synthetic polymer; Positively charged polyacrylamide.







